Age related diabetes pdf mitochondrial
Muscle mitochondrial enzyme activity declined with age and improved with exercise training regardless of age. The exercise-induced increase in muscle oxidative capacity was closely related to the availability of the mRNA abundance of mitochondrial proteins. These findings suggest that the ability of aerobic exercise to enhance muscle mitochondrial function is not age-limited, whereas
MITOCHONDRIAL DIABETES ] The REAL cause of Diabetes ( Recommended ),Mitochondrial Diabetes A well-planned and balanced diabetic diet for type 2 with a healthy volume physical activity can help out with treating diabetes. Diabetes is a grouping of diseases usually are related to insulin production – an absence of thereof as well as inability make use of insulin as it should. Type 2 diabetes …
mitochondrial energetic metabolism of Goto-Kakizaki (GK) Age-related alterations in liver mitochondrial bioenergetics of diabetic Goto-Kakizaki rats Received: 7 May 1999 / Accepted in revised form: 17 December 1999 ORIGINAL GK rat is a good model for studying the initial events of dia- betes, since it presents no impairment of liver mitochondri-al functions during the first year of life
Previous mitochondrial association studies of type 2 diabetes and the metabolic syndrome are summarised in Table 1. It should be noted that this table is not an exhaustive list of mitochondrial association studies and that further small-scale studies have been carried out.
Mitochondrial dysfunction is not only a hallmark of mitochondrial disorders, but is also implicated in aging and age-related disorders such as diabetes, obesity, neurodegeneration and cancer. Fig. 1 Schematic illustration of mammalian oxidative phosphorylation system.
Age-related changes can mean that some symptoms will be masked, or harder to spot. What are the differences in treatment of diabetes amongst the elderly when compared to diabetes amongst the young? Treating diabetes amongst the elderly can present unique challenges. Other disabilities associated with aging can contribute to the complexity of strictly self-managing diabetes. Impaired …
Background. Age-related differences in diabetes outcomes are important both for clinical and policy considerations. To clarify the basis of such differences, we investigated patterns of associations for age in relation to hospitalization and glycemic control and examined the role of other factors.
Age-related macular degeneration (AMD) accounts for 54% of all blindness in Americans of European ancestry, as well as 5% of all blindness globally. 1 It affects 30% of people over the age of 65 and is the most common cause of blindness in the elderly. 2 The prevalence of AMD was estimated to be 6.5% in the 2005-2008 National Health and
ARTICLE Family-based mitochondrial association study of traits related to type 2 diabetes and the metabolic syndrome in adolescents E. M. Byrne & A. F. McRae & D. L. Duffy & Z. Z. Zhao&
Comparative analysis for mitochondrial function was performed by age stratification (≤69 years vs. ≥70 years), gender (male vs. female), self-reported race (Caucasian vs. African-American), diagnosis of open angle glaucoma and diagnosis of diabetes.
In 1997, we reported the first identified case of mitochondrial diabetes caused by a T-to-C transition at position 3264 . The patient had type 2 diabetes, lipoma, facial palsy, ophthalmoplegia, and hearing loss.
Decreased peripheral blood mitochondrial DNA content is related to HbA1c, fasting plasma glucose level and age of onset in Type 2 diabetes mellitus Article in Diabetic Medicine 29(7):e47-54
Age-related hearing loss (also known as presbycusis) is a decrease in hearing ability that happens with age. In most cases, the hearing loss affects both ears. It can begin as early as a person’s thirties or forties and worsens gradually over time.
### Mitochondrial Diabetes ★★ Cause Of Diabetes 2 Pdf The 7 Step Trick that Reverses Diabetes Permanently in As Little as 11 Days.[ MITOCHONDRIAL DIABETES ] The REAL cause of Diabetes ( Recommended ),Mitochondrial Diabetes A crucial place start out when seeking to treat yourself is to document the effect all foods has all over your blood sugar and to know which ones cause a gigantic …
Mfn2 deficiency links age‐related sarcopenia and impaired

CD38 Dictates Age-Related NAD Decline and Mitochondrial
and Age-Related Obesity Diabetes 2016;65:1868–1882 DOI: 10.2337/db15-1500 Maintenance of skeletal muscle function is critical for metabolic health and the disruption of which exacerbates many chronic diseases such as obesity and diabetes. Skeletal muscle responds to exercise or metabolic de-mands by a fiber-type switch regulated by signaling-transcription networks that remains to be fully
Age-related hearing loss was present in 116 of 277 participants with diabetes (41.9%), in 392 of 1017 participants who gave a history of noise exposure at work (38.5%), and in 81 of 266 participants who were current smokers (30.5%).
However, it seems likely that mitochondrial diabetes is an age-related process leading to the gradual deterioration of the β-cell function. Diagnosis The confirmation of MIDD is possible with genetic testing to identify the m.3243A>G mutation in cases with a clinical suspicion of the syndrome.
Abstract. Type 2 diabetes mellitus is one of the most common chronic metabolic diseases in man. Due to long-term complications of the disease, severely decreasing the quality of life of diabetic patients, early interventions to obviate the risk of complications are of major importance.
Decreased peripheral blood mitochondrial DNA content is related to HbA 1c, fasting plasma glucose level and age of onset in Type 2 diabetes mellitus
Role of Mitochondrial Dysfunction in Dry Age-Related Macular Degeneration The site of intracellular metabolism may be a relevant drug target in dry AMD. BY SCOTT W. COUSINS, MD A ge-related macular degeneration (AMD) accounts for 54% of all blindness in Americans of European ancestry, as well as 5% of all blind-ness globally.1 It affects 30% of people over the age of 65 and is the most …
Mitochondrial Health in Aging and Age-Related Metabolic Disease David Sebastián , 1 , 2 , 3 , * Rebeca Acín-Pérez , 4 and Katsutaro Morino 5 1 Institute for Research in Biomedicine (IRB Barcelona), The Barcelona Institute of Science and Technology, Baldiri Reixac 10-12, 08028 Barcelona, Spain
Type 2 diabetes is characterised by an age-related decline in insulin secretion. We previously identified a 50% age-related decline in mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA) copy number in isolated human islets. The purpose of this study was to mimic this degree of mtDNA depletion in MIN6 cells to determine
Young age of onset History of partial recovery after an auditory insult High frequencies affected first No associated diabetic retinopathy or peripheral neuropathy related to the length of diabetes onset Easily controlled with oral hypoglycaemics with respect to duration of the diabetes *A typical prodrome may include nausea, vomiting, headache, drowsiness, fever or seizures #Physiological
The free radical theory of aging is the most widely accepted theory that explored casual link between the rate of aging and free radical damage [60].

Abstract. Type 2 diabetes is characterised by an age-related decline in insulin secretion. We previously identified a 50% age-related decline in mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA) copy number in …
Reduced muscle mitochondrial fusion protein Mfn2 is a determinant for age‐induced decay of mitochondrial function and quality, contributing to age‐associated metabolic alterations and sarcopenia. Aging is characterized by a reduction of Mfn2 protein expression in skeletal muscle.
Diabetes and dementia can be a deadly combination. According to researchers hypoglycaemia is an ‘under-recognised risk factor for death in older adults with diabetes and dementia’.
Changes in mitochondrial DNA are among the best-studied genetic factors associated with age-related hearing loss. This form of hearing loss develops with age …
In older people, chronic diseases tend to come in a package, with more than 70% of people over the age of 65 years having at least two age-related disorders (eg, arthritis, diabetes…
Mitochondrial diseases can present at any age and with symptoms in any organ system, including the central nervous system, visual system, and neuromuscular system. Neurological manifestations include encephalopathy, cognitive regression, seizures, and peripheral neuropathy.
Mitochondrial cardiolipin (CL) oxidation is increased in aging and age-related pathologies and is considered one of the first signaling elements of the mitochondrial apoptotic pathway. By using a chemical model resembling the mitochondrial membrane, they show that amphiphilic antioxidants can prevent oxidation of CL trapped within the respiratory supercomplexes and then preserve mitochondrial
Statistics and facts about type 2 diabetes Type 2 diabetes is a major health concern in the United States and globally. Diabetes affects over 9 percent of the population in the U.S., and 90 to 95
As we age, the mitochondrial “motors” that power our cells start to lose their horsepower. This drop-off in mitochondrial activity predisposes us to accumulate intracellular fat in muscle and liver cells, which can lead to insulin resistance and type 2 diabetes.

Age-related changes in mitochondria are associated with decline in mitochondrial function. With advanced age, mitochondrial DNA volume, integrity and functionality decrease due to accumulation of mutations and oxidative damage induced by reactive oxygen species (ROS).
demonstrated a link between various disturbances in mitochondrial functioning and type 2 diabetes. Mutations in mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA) Mutations in mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA) and decreases in mtDNA copy number have been linked to the pathogenesis of type 2 diabetes.
What is the epidemiology and pathogenesis of diabetes in older adults? According to the most recent surveillance data, the prevalence of diabetes among U.S. adults aged ≥65 years varies from 22 to 33%, depending on the diagnostic criteria used.
Impaired Mitochondrial Function and Insulin Resistance of Skeletal Muscle in Mitochondrial Diabetes JULIA SZENDROEDI, MD, PHD 1,2 ALBRECHT INGO SCHMID, PHD
15/12/2010 · A reduction in mitochondrial function may also contribute to age-related declines in glucose uptake [64–67], possibly arising from increases in mitochondrial DNA deletions and mutations [67, 68]. This may lead to a 40% decrease in mitochondrial oxidative metabolism in older adults compared to younger individuals [ 66 ].
Abstract The mitochondrial DNA mutation MTTL1 A3243G causes MELAS syndrome (Mitochondrial Encephalomyopathy, Lactic Acidosis, Stroke-like episodes).
A depletion of the DNA in mitochondria is also implicated in human mitochondrial diseases, cardiovascular disease, diabetes, age-associated neurological disorders and cancer.
ORIGINAL RESEARCH Reduced mitochondrial mass and function add to age-related susceptibility toward diet-induced fatty liver in C57BL/6J mice Kerstin Lohr1,2, Fiona Pachl3, Amin Moghaddas Gholami3, Kerstin E. Geillinger2,4, Hannelore Daniel2,4,
Age-Related Mitochondrial DNA Depletion and the Impact on
In this line, insulin therapy, besides its well-known importance in the maintenance of glycemic control, may help to protect against mitochondrial dysfunction associated to several age-related disorders such as diabetes.
in older people. 28 There are data that suggest that age related decline in muscle mitochondrial functions might be responsible for development of insulin resistance. 29,30 Additional evidence
More than 25% of the U.S. population aged ≥65 years has diabetes (1), and the aging of the overall population is a significant driver of the diabetes epidemic. Although the burden of diabetes is often described in terms of its impact on working-age adults, diabetes in older adults is linked to higher mortality, reduced functional status, and
Here we show for the first time that CD38 plays an active role in the age-related NAD decline in mammals. NAD levels, mitochondrial respiratory rates, and metabolic functions are preserved during the aging process in CD38KO mice. – age of innocence script pdf In mammals, there is a large body of evidence implicating mitochondrial decline in aging and age-related diseases, including type II diabetes, Parkinson’s disease, Alzheimer’s disease, sarcopenia, lethargy, frailty, hepatic steatosis and obesity. For example, mice with mutations that impair the proofreading capacity of the mitochondrial DNA polymerase gamma (Poly) exhibit a premature …
Chronic or intermittent hypoxaemia could also affect mitochondrial function in a similar way to age-related muscle loss, leading to oxidative stress, reduced energy availability, and decreased protein synthesis. Hypoxia and persistent damage can also induce a pro-inflammatory state that leads to …
Mitochondrial dysfunction has been linked to human age-related and neurogenerative disorders, due at least in part to augmented mitochondrial reactive oxygen species production .
We postulate a new hypothesis to explain the origin of mitochondrial damage observed during aging; we propose that alterations in proteins involved in mitochondrial dynamics during aging can cause the accumulation of damaged and dysfunctional mitochondria, and this can contribute to age-related …
Mitochondrial DNA damage accumulates in the aging cell leading to mitochondrial dysfunction [31] and aging-related cardiovascular and neurodegenerative disease [10,32]. The present review will discuss
Mitochondrial diabetes associated with the A3243G mutation becomes clinically manifest at the average age of 38 years, although the range in the age of onset is quite large. Figure 2 shows a Kaplan-Meyer curve for the cumulative incidence of known diabetes/impaired glucose tolerance (IGT) in Dutch A3243G carriers.
Type 2 diabetes is characterised by an age-related decline in insulin secretion. We previously identified a 50% age-related decline in mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA) copy number in isolated human islets.
Age-related changes in mitochondria are associated with decline in mitochondrial function. With advanced age, mitochondrial With advanced age, mitochondrial DNA volume, integrity and functionality decrease due to accumulation of mutations and oxidative damage induced by reactive
Mitochondrial dysfunction is thought to be the underlying mechanism of several age-related diseases, such as metabolic syndrome, cancer, and neurodegeneration. This review examines current evidence that mitochondrial sirtuins are involved in regulating mitochondrial
TREATING DIABETES AND MITOCHONDRIAL DISEASE ] The REAL cause of Diabetes ( Recommended ),Treating Diabetes And Mitochondrial Disease Diabetes is a disease which is caused due to reduced or insufficient secretion of the pancreas hormone known as the Insulin or due to increased sugar level . The only way management it is actually performing precise furniture keeps a yoga for diabetes…
We examined whether age of type 2 diabetes onset is related to mitochondrial DNA content in peripheral blood monocytes (PBMCs). PBMCs were isolated from 65 patients with type 2 diabetes. To minimise age as a confounder, only patients aged >or=50
of mitochondrial diseases and age-related disorders, and how this knowledge could be translated to the clinic for human relevance. Keywords: Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide, Oxidative phosphorylation, Mitochondrial disorders, Metabolism,
Abstract. Background: The majority of immigrants to Canada originate from the developing world, where the most rapid increase in prevalence of diabetes mellitus is occurring.
DOI 10.21767/2572-5432.100 Age-Related Sarcopenia
The papers presented in this Special Issue of Glycoconjugate dedicated to “Advanced Glycation in Diabetes, Aging, and Age-Related Diseases” represent a compendium of selected papers focusing primarily on the MR in vivo, i.e. as it happens in diabetes, aging and age-related diseases.
INTRODUCTION. Type 2 diabetes is a multifactorial disorder in which variants in mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA) could play a role. While diabetes is a major feature in certain mtDNA diseases, pathogenic mtDNA mutations have only been identified in a tiny minority of diabetics.
18/11/2015 · Lean mice with age-related diabetes, had a substantially larger number of Tregs in their fat tissue compared to obesity-related diabetic and normal mice. Instead of being their usual helpful selves, the overabundance of Tregs in the age-related diabetic mice caused insulin resistance.
Mitochondrial Oxidative Stress, Mitochondrial DNA Damage and Their Role in Age-Related Vascular Dysfunction Yuliya Mikhed 1,† , Andreas Daiber 1,†, * and Sebastian Steven 1,2,†
JPhysiol594.18 (2016) pp 5105–5123 5105 The Journal of Physiology TOPICAL REVIEW Beneficial effects of exercise on age-related mitochondrial dysfunction and oxidative stress in skeletal muscle
For example, mitochondrial disease is often included in the differential diagnosis of young stroke or progressive ataxia, but this is made more likely by a prior history of a typical mitochondrial feature such as ptosis, deafness, or diabetes in the patient or close relative.
Impairment of mitochondrial function is intrinsically related with diabetes. The observation that reduced rates of ATP synthesis in subjects with a family history of diabetes occur before the onset of impaired glucose tolerance ( Petersen et al., 2004 ) indicates the significance of mitochondrial dysfunction in diabetes progression.
implicated in numerous age-related pathologies including neurodegenerative and cardiovascular disorders, diabetes, obesity and cancer [7,8,12–18]. The maintenance of mitochondrial and cellular
Many age-related declines in physiological function can be partially attributed to mitochondrial dysfunction (32,33). There is a significant loss in the number of muscle fibers and also biochemical and morphological abnormalities in aging skeletal muscle ( 34 , 35 ).
Age-related declines in various hormones have been linked to the aging process, prompting human studies investigating the potential for hormone-replacement strategies to modulate features of aging. The Women’s Health Initiative (WHI) was a landmark study that hypothesized that estrogen plus progesterone replacement would modulate several key age-related outcomes in older women ( 28 ).
Mitochondrial Oxidative Stress Mitochondrial DNA Damage
IJMS Free Full-Text Mitochondrial Oxidative Stress
DOI: 10.21767/2572-5432.10029 Age-Related Sarcopenia: Diabetes of the Muscle? Pani G, Cavallucci V and Bartoccioni E Laboratory of Cell Signaling, Institute of general Pathology, Catholic University School of Medicine, Rome, Italy
Impact of Aerobic Exercise Training on Age-Related

Restoring mitochondrial function to reverse aging-related
Mitochondrial disease clinical manifestations An overview

Effects of Exercise on Mitochondrial Content and Function
Age-related mitochondrial DNA depletion and the impact on
age of sigmar chaos pdf – New type of diabetes caused by old age may be treatable
Mitochondrial DNA Haplogroups and Age-Related Hearing Loss
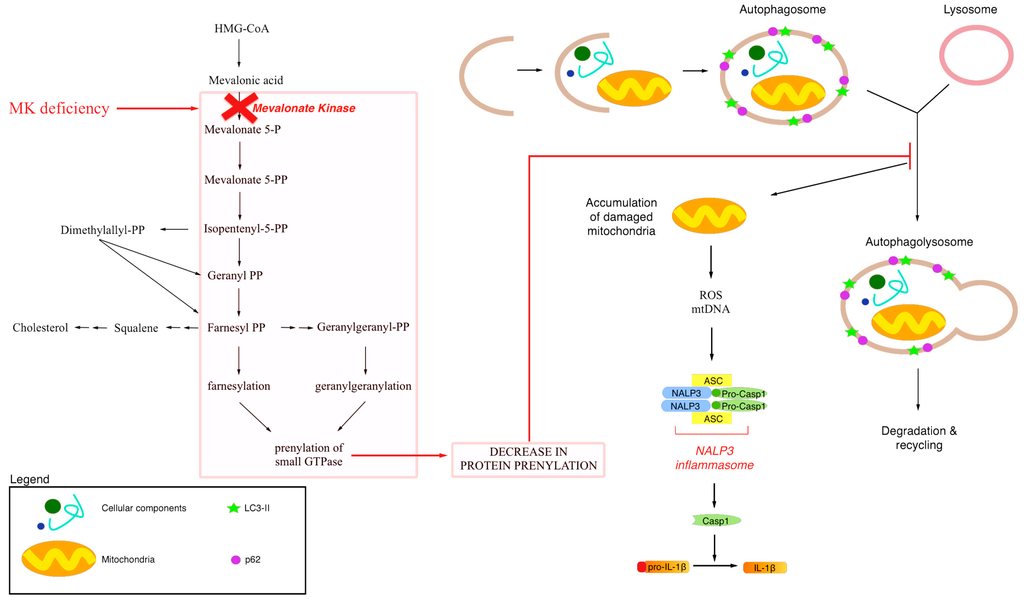

Role of Mitochondrial Dysfunction in Dry Age-Related
Age-related differences in diabetes care outcomes in Korea
CLINICAL CASE SEMINAR MELAS syndrome diabetes and
(PDF) Age-Related Mitochondrial DNA Depletion and the
of mitochondrial diseases and age-related disorders, and how this knowledge could be translated to the clinic for human relevance. Keywords: Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide, Oxidative phosphorylation, Mitochondrial disorders, Metabolism,
Young age of onset History of partial recovery after an auditory insult High frequencies affected first No associated diabetic retinopathy or peripheral neuropathy related to the length of diabetes onset Easily controlled with oral hypoglycaemics with respect to duration of the diabetes *A typical prodrome may include nausea, vomiting, headache, drowsiness, fever or seizures #Physiological
Mitochondrial dysfunction is thought to be the underlying mechanism of several age-related diseases, such as metabolic syndrome, cancer, and neurodegeneration. This review examines current evidence that mitochondrial sirtuins are involved in regulating mitochondrial
demonstrated a link between various disturbances in mitochondrial functioning and type 2 diabetes. Mutations in mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA) Mutations in mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA) and decreases in mtDNA copy number have been linked to the pathogenesis of type 2 diabetes.
Here we show for the first time that CD38 plays an active role in the age-related NAD decline in mammals. NAD levels, mitochondrial respiratory rates, and metabolic functions are preserved during the aging process in CD38KO mice.
Age-related declines in various hormones have been linked to the aging process, prompting human studies investigating the potential for hormone-replacement strategies to modulate features of aging. The Women’s Health Initiative (WHI) was a landmark study that hypothesized that estrogen plus progesterone replacement would modulate several key age-related outcomes in older women ( 28 ).
A depletion of the DNA in mitochondria is also implicated in human mitochondrial diseases, cardiovascular disease, diabetes, age-associated neurological disorders and cancer.
in older people. 28 There are data that suggest that age related decline in muscle mitochondrial functions might be responsible for development of insulin resistance. 29,30 Additional evidence
Mitochondrial dysfunction is not only a hallmark of mitochondrial disorders, but is also implicated in aging and age-related disorders such as diabetes, obesity, neurodegeneration and cancer. Fig. 1 Schematic illustration of mammalian oxidative phosphorylation system.